If younger men are more likely to develop erectile dysfunction
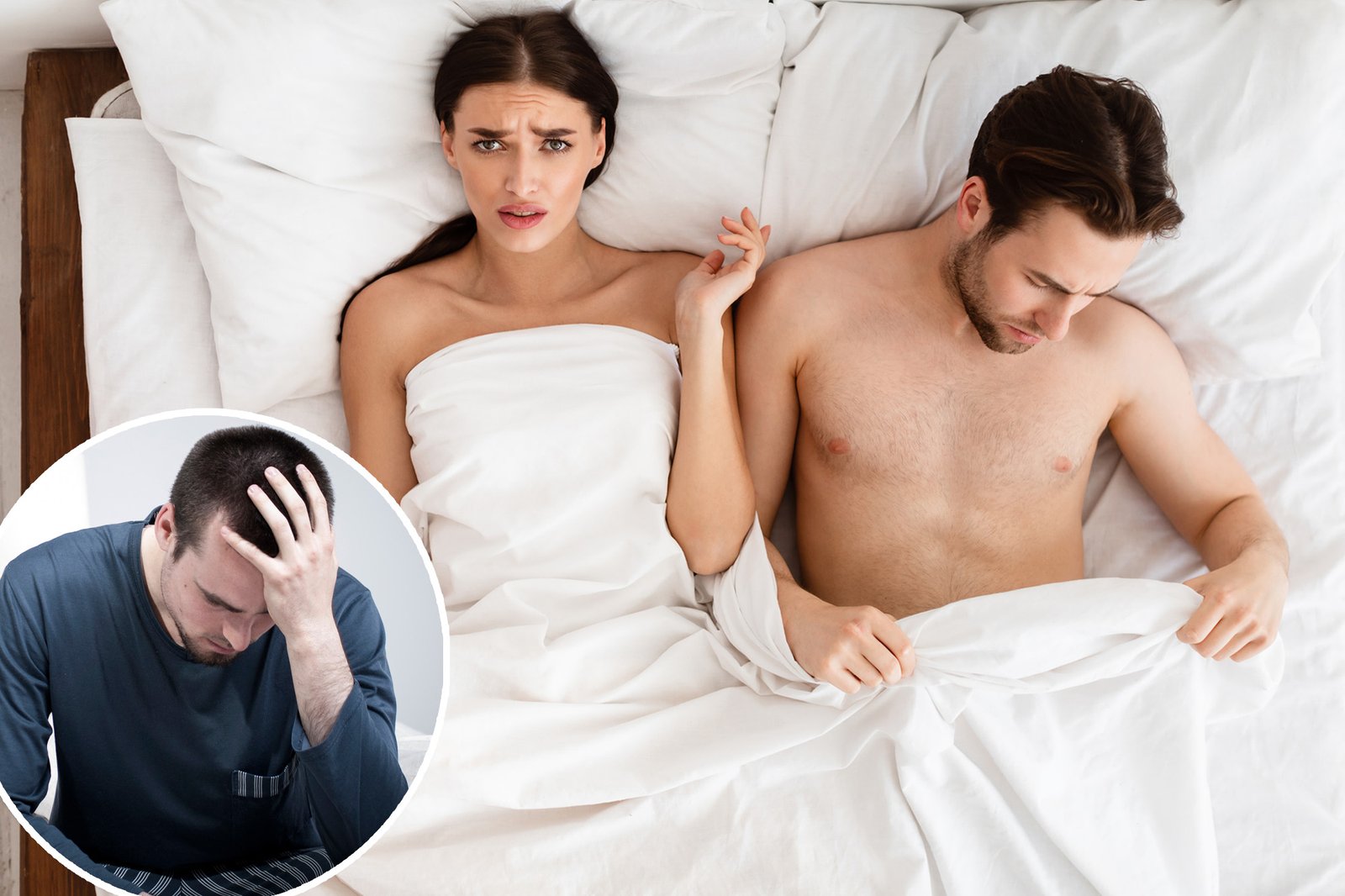

As if erectile dysfunction (ED) wasn’t bad enough, scientists say impotence may be linked to a common disorder that causes humiliatingly persistent symptoms.
ED occurs when you are unable to get or keep an erection hard enough for satisfying sex, affecting approximately 30 million American men. It can be caused by psychological problems (such as stress or past trauma), physical problems (such as diabetes or neurological problems), medications, or drug use.
Now, scientists are exploring potential links between ED and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a chronic gastrointestinal disorder believed to affect 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. population.
In a small study of medical students, Peruvian researchers determined that people with IBS had a 108 percent higher prevalence of ED than those without stomach problems.
The study authors note that medical students often face overwhelming academic demands. Stress can significantly affect the production of sex hormones, especially testosterone, and disrupt the coordination between nerves and blood vessels needed for an erection.
They also note that people with IBS often have a poor quality of life because embarrassing symptoms such as uncontrollable gas, diarrhea and bloating seriously affect their mental health and undermine their desire for sexual arousal.
In addition to psychological factors, possible explanations include changes in gut hormones associated with irritable bowel syndrome, which can affect blood flow and nerve signaling, as well as problems with the lining of blood vessels.
Another study in 2024 confirmed that inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may cause ED.
IBD is similar to IBS in that it is a chronic digestive disease, but IBS does not cause inflammation.
An estimated 2.4 million to 3.1 million Americans have IBD.
The study authors believe that Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract, may increase the risk of ED, while ulcerative colitis may not.
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in the colon and rectum. The study authors said further research is needed to clarify the cause-and-effect relationship between IBD and ED.
There is currently no known treatment for IBD or IBS.
Patients can find relief from symptoms with medications, a healthier diet, and lifestyle changes such as managing stress and drinking more fluids. People with IBD sometimes need surgery.
In the meantime, men with ED may benefit from oral medications, exercise, alcohol withdrawal, psychosexual counseling, or surgery.


 Anal Beads
Anal Beads Anal Vibrators
Anal Vibrators Butt Plugs
Butt Plugs Prostate Massagers
Prostate Massagers
 Alien Dildos
Alien Dildos Realistic Dildos
Realistic Dildos
 Kegel Exercisers & Balls
Kegel Exercisers & Balls Classic Vibrating Eggs
Classic Vibrating Eggs Remote Vibrating Eggs
Remote Vibrating Eggs Vibrating Bullets
Vibrating Bullets
 Bullet Vibrators
Bullet Vibrators Classic Vibrators
Classic Vibrators Clitoral Vibrators
Clitoral Vibrators G-Spot Vibrators
G-Spot Vibrators Massage Wand Vibrators
Massage Wand Vibrators Rabbit Vibrators
Rabbit Vibrators Remote Vibrators
Remote Vibrators
 Pocket Stroker & Pussy Masturbators
Pocket Stroker & Pussy Masturbators Vibrating Masturbators
Vibrating Masturbators
 Cock Rings
Cock Rings Penis Pumps
Penis Pumps
 Wearable Vibrators
Wearable Vibrators Blindfolds, Masks & Gags
Blindfolds, Masks & Gags Bondage Kits
Bondage Kits Bondage Wear & Fetish Clothing
Bondage Wear & Fetish Clothing Restraints & Handcuffs
Restraints & Handcuffs Sex Swings
Sex Swings Ticklers, Paddles & Whips
Ticklers, Paddles & Whips